Introduction
Dental infections can be a source of significant discomfort and health issues if not properly managed. Understanding the most common types of dental infections and knowing how to prevent and control them can help maintain good oral health. This article will explore common dental infections, their causes, symptoms, and effective strategies to control and prevent them.
Definition
The term “dental infection control” describes the procedures and guidelines used to stop infections from spreading in dental environments. In order to reduce the chance of disease transmission between patients and dental healthcare practitioners, it entails strict hygiene precautions, sterilisation of instruments, and usage of personal protective equipment (PPE). A safe environment for dental treatments is ensured by effective infection control, which also shields patients and dental workers from possible infections.
Dental Caries (Tooth Decay)
Causes: Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth. These bacteria produce acids that erode the enamel, leading to cavities.
Symptoms:
- Toothache or spontaneous pain
- Food and beverage sensitivity to sweet, cold, or hot
- Visible holes or pits in the teeth
- Brown, black, or white staining on the tooth surface
Prevention and Control:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth at least twice a day, and floss every day to get rid of food particles and plaque.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups to catch early signs of decay.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary snacks and drinks, as sugar feeds the bacteria that cause tooth decay. Choose a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products that is well-balanced.
- Fluoride Treatments: Use fluoride mouthwash or get professional fluoride treatments to strengthen tooth enamel.
Gingivitis
Causes: Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup at the gumline. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe periodontal diseases.
Symptoms:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
Prevention and Control:
- Consistent Oral Care: Maintain a routine of brushing and flossing to remove plaque and prevent gum inflammation.
- Professional Cleanings: Regular dental cleanings can remove tartar (hardened plaque) that cannot be removed by brushing alone.
- Antibacterial Mouthwash: Using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and control gum inflammation.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Avoid smoking and manage conditions like diabetes that can increase the risk of gum disease.
Periodontitis
Causes: Periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. It affects the tissues and bones that support the teeth.
Symptoms:
- Receding gums are gums that separate from the teeth.
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Persistent bad breath
Prevention and Control:
- Early Intervention: Treat gingivitis promptly to prevent progression to periodontitis.
- Scaling and Root Planing: Professional deep cleaning procedures can remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline.
- Surgical Treatments: In severe cases, surgical treatments like flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be necessary.
- Medication: Antibiotic treatments may be prescribed to control bacterial infection.
Dental Abscess
Causes: A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. It can occur in different parts of the tooth or gum and is often the result of untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or dental trauma.
Symptoms:
- Severe, persistent, throbbing toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Swelling in the face or cheek
- tender, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or beneath the jaw
Prevention and Control:
- Prompt Dental Care: Seek immediate dental care if you experience symptoms of an abscess. Delays may result in more severe issues.
- Root Canal Treatment: This procedure removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth to prevent further infection.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed antibiotics can help clear the infection and prevent it from spreading.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases, the affected tooth may need to be extracted.
Candidiasis (Oral Thrush)
Causes: Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida yeast. It can occur when the natural balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted.
Symptoms:
- Creamy white lesions on the tonsils, roof of the mouth, gums, and inside cheeks occasionally
- Redness or pain that could make it difficult to swallow or eat
- The corners of your mouth are red and cracked.
Prevention and Control:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the mouth.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugar intake, as high sugar levels can promote yeast growth.
- Medication: Antifungal medications prescribed by a dentist or doctor can treat oral thrush.
- Monitor Health Conditions: Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes and avoid excessive use of antibiotics or corticosteroids, which can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections
Causes: Cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth can result from an infection with the herpes simplex virus. The virus is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person.
Symptoms:
- Painful blisters or ulcers on the lips or around the mouth
- Tingling or stinging feeling prior to the development of sores
- Fever, swollen lymph nodes, and general malaise during initial infection
Prevention and Control:
- Avoid Direct Contact: Avoid close contact with individuals who have active cold sores.
- Personal Hygiene: Do not share personal items like toothbrushes, lip balm, or utensils with someone who has a cold sore.
- Antiviral Medications: Prescription antiviral medications can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
- Stress Management: Manage stress and maintain a healthy immune system to reduce the likelihood of outbreaks.
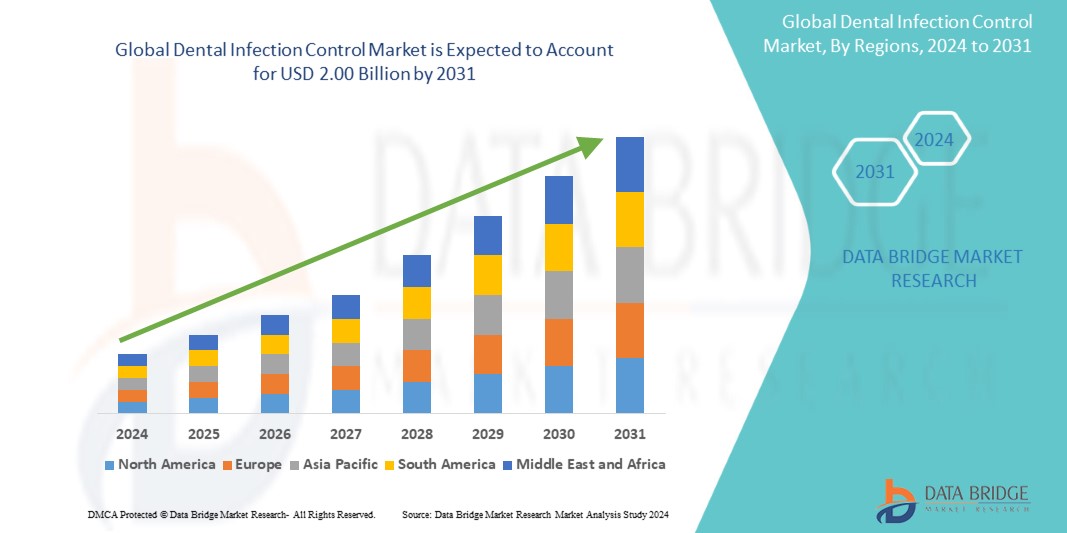
Growth Rate of Dental Infection Control Market
The size of the worldwide market for dental infection control was estimated at USD 1.30 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 2.00 billion.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-dental-infection-control-market
Conclusion
Dental infections, though common, can lead to serious health issues if not properly managed. Practicing good oral hygiene, maintaining regular dental check-ups, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are crucial in preventing and controlling these infections. Early intervention and professional treatment are key to managing symptoms and preventing complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for common dental infections, you can take proactive steps to ensure optimal oral health and overall well-being.